Alzheimer’s Disease Research Antibodies
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by progressive cognitive dysfunction and memory loss. The disease is first described in 1906 and named by German psychiatrist and pathologist Alois Alzheimer. In 2020, there were approximately 50 million Alzheimer's disease patients worldwide.
During the past dozen years, a steadily accumulating body of evidence has indicated that soluble forms of Aβ and tau work together, independently of their accumulation into plaques and tangles, to drive healthy neurons into the diseased state and that hallmark toxic properties of Aβ require tau. The behavioral symptoms of AD correlate with the accumulation of plaques and tangles, and they are a direct consequence of the damage and destruction of synapses that mediate memory and cognition.(George. B, 2014)
Amyloid-β
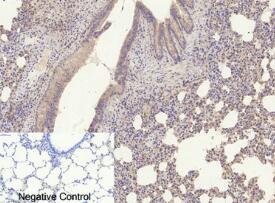
Amyloid-β peptides are the main component of the amyloid plaques found in the brains of Alzheimer's disease patients. Aβ plays a critical role and may be an upstream molecule in AD pathogenesis involving both genetic and environmental factors.
BT-AP06254-Amyloid-beta Polyclonal Antibody
BT-AP00086-Amyloid-beta Polyclonal Antibody
Tau
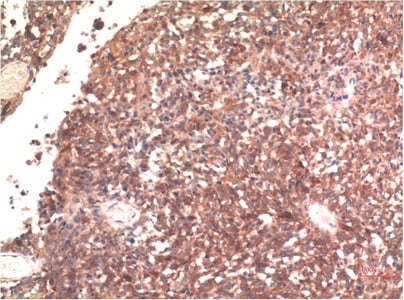
Tau is a brain-specific, axon-enriched microtubule-associated protein and plays a primarily role in maintaining the stability of microtubules in axons and is abundant in the neurons of the central nervous system (CNS).
BT-MCA1185-Tau(10E3) Monoclonal Antibody
BT-AP14778-Tau Polyclonal Antibody
BT-AP14768-Tau(Phospho Thr534) Polyclonal Antibody
BT-AP14767-Tau(Phospho Thr212) Polyclonal Antibody
BT-AP07513-Tau(Phospho Thr231) Polyclonal Antibody
